Introduction
Requirements management is one of the most essential cornerstones of any project or business. Its importance in team management is often underestimated. However, knowing and understanding it means that you will have a precious advantage compared to your competitors.
In this article, you will learn about the role of requirements management in projects, particularly within the context of software development. We'll look at effective requirements management practices, IBM requirements management tools, and the key requirement management process steps that help teams maintain control over project scope and objectives. Understanding why requirements management is important and how to implement it successfully can significantly improve your chances of project success and provide real value for your organization.
What is requirements management?
Definition
The very basic concept of requirements management (RM) is something that we do our whole lives, almost every day. Even though it’s a simplified version of it, even doing our school assignments was partly an RM process. We gathered requirements in the form of assignments and test material for a specific class, captured them into our notes, and then tried to follow and satisfy these requirements in an organized way (making projects and preparing for tests).
Based on this example, we can also understand requirements management as a process of capturing, documenting, and managing the requirements of a project throughout its lifecycle. It encompasses various actions and processes to make sure that the project requirements are correctly identified, understood, and fulfilled through effective management.
Aspects of project requirements management
Requirements are an extension of the needs of your stakeholders (customers, investors, partners, etc.) for your project to accomplish a task or display quality. They are the “results” that your project must accomplish in a given context, for example, to have a feature that functions in a specific way:
Requirement: User Authentication
Description: The system shall provide a secure user authentication mechanism to ensure that only authorized users can access the application.
Since every project is connected to a certain number of stakeholders, there will be a substantial amount of generated requirements. At best, there will be an easily manageable number of requirements for smaller and less complex projects.
However, larger and more complex projects usually involve a very large volume of project requirements since there will be more stakeholders, each with more needs to satisfy for that specific project.
For this reason, proper team management is the difference between not being able to tackle the requirements management difficulties and successfully completing the project. In the context of project requirements management, team management involves organizing and enabling communication among project team members who are in charge of gathering, interpreting, and verifying requirements. It involves delegating duties, keeping track of progress, settling issues, and maintaining clear communication among team members. It is one of the most important but undervalued aspects of the requirements management process, since without it, larger projects with many complex requirements have no chance of meeting deadlines and completing project requirements.
The last important and often overlooked aspect of requirements management is change management. Throughout the project's lifetime, requirements might change. Assessing suggested change effects on project needs, determining their viability, and carrying them out while limiting risks are all parts of change management. It ensures that requirements are updated and in line with shifting needs for the project.
The importance of requirements management
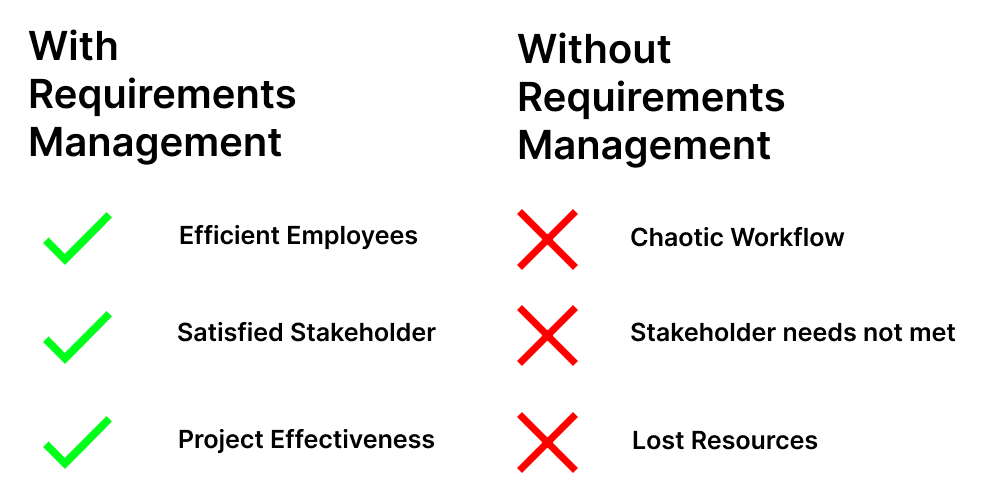
On a basic level, the importance of requirements management can be best understood by the fact that if you lack it, your projects will cost more and fail more.
However, it can also be explained on a practical level with an example of a business that does take care of requirements management and one that doesn’t.
In a business where the requirements management process is on point, the requirements of the stakeholders are processed, properly understood, and taken care of by the employees on a given project. The employees have a clear understanding of what needs to be done, and the stakeholders are satisfied with the results of the project since their needs have been adequately reflected and taken care of.
Now let’s compare it with a business where the importance of requirements management is neglected. The needs of stakeholders are not properly transformed into comprehensible project requirements; they are not well documented, and so the employees have little idea of what is actually expected of them by the stakeholders. This results in frustration on the part of the employees. Since they had to improvise and couldn’t properly fulfill the expectations of the stakeholders, dissatisfaction will be present when the projects are finished since the needs of the stakeholders have not been met. No business can effectively operate like this.
Even though this is a worst-case scenario, undervaluing requirements management and its importance can cause you to not benefit from the many advantages that a properly developed requirements management process brings to the table.
To point out a few:
- Requirements management guarantees that stakeholder demands are well understood, which aids in determining the project's scope and goals. It reduces uncertainty and encourages productive dialogue between the team and stakeholders, making team management easier and more efficient.
- A properly managed requirements management process aids in the early identification and control of possible hazards. Teams can spot possible problems, dependencies, and conflicts by carefully studying and validating requirements, allowing for prompt risk mitigation steps.
- By identifying and ranking project requirements, requirements management allows effective scope control. It aids in managing changes, controlling scope expansion, and making sure project deliverables achieve the expected results.
Effective requirements management helps with project effectiveness. Teams may increase productivity and overall project performance by having a comprehensive grasp of requirements. This allows teams to make well-informed choices, allocate resources wisely, and simplify project operations, again making team management more effective.
The phases of a requirements management process
The six phases of the requirements management process include crucial steps designed to ensure the accurate and effective handling of projects requirements.
The Continuous phase: communication is key
Requirements communication is an essential component of requirements management, even if it isn't technically a phase. It involves clearly outlining the needs of each project stakeholder, establishing understanding, and promoting cooperation. Common knowledge of the project requirements is fostered by clear and concise communication, which also helps prevent misconceptions and provides consistency.
2.) Visualization of Requirements Management Phases
1. Planning phase
Requirements management planning involves creating an extensive requirements management plan. The method for compiling, establishing priorities for, organizing, regulating, and approving requirements is described in this plan. Stakeholder involvement, team management techniques, and project methodology are also taken into account. Planning guarantees a clearly defined and goal-aligned requirements management process.
2. Requirements identification phase
In this step, all stakeholders are identified, and their requirements and expectations are established. To gather needs, the company utilizes methods that include one-on-one interviews, focus groups, surveys, and use cases. In order to ensure that all project requirements are fully understood, the project management team works with stakeholders to identify and record their system needs.
3. Requirements documentation
In requirements management, to prevent relying on people's memories or interpretations, project requirements must be consistently recorded after being recognized. All agreed-upon criteria are written down and given special identification numbers by the business analyst or other project personnel in order to be tracked throughout the process.
Requirement specifications, use cases, diagrams, and other artifacts that precisely specify the expected system behavior should all be included in the documentation to make task delegation and team management easier.
4. Requirements prioritization
Prioritizing requirements is essential to properly managing project scope and resource allocation. During this stage, each project requirement's relative relevance, urgency, and business value are evaluated using the information and insights acquired from the requirements analysis. The most important requirements are given the proper attention and resources thanks to prioritization and team management
5. Requirements control
Managing requirements changes throughout the course of a project is known as requirements control. Some requirements might need to be changed or added when new information or project requirements arise. The project manager evaluates the effects of suggested modifications, takes into account restrictions like time and money, and then modifies the requirements as necessary together with the project team. This stage makes ensuring that requirements are up-to-date and in line with the goals of the project easier.
6. Requirements approval
The final step of requirements management, the approval process, entails securing written authorization for the suggested requirements from any relevant parties. Making sure that all authorizations are received and accurately recorded is mostly the responsibility of the project manager.
Stakeholders can use this material as a point of reference and to create consensus on the accepted requirements. The approval gives the necessary permission to proceed with implementing the requirements.
Requirements management tools
Requirements management tools, like IBM DOORS, play a key role in the requirements management process. These tools include a variety of capabilities and features that help with requirement gathering, analysis, documentation, and implementation. They offer one convenient place where project requirements may be kept, arranged, and maintained, making it simple for team members engaged in requirements management to access and collaborate with one another, simplifying team management.
Version control and change management are also benefits of requirements management tools. They provide effective change management by maintaining prior versions and allowing teams to trace changes made to requirements over time. Team members may evaluate and contrast several revisions of requirements, tracking changes and making sure they are all handled effectively.
Requirements management tools are a must-have for larger and more complex projects, as they are impossible to be managed through documents and other ways of documenting requirements.
3.) Key Takeaways From The Article
Conclusion
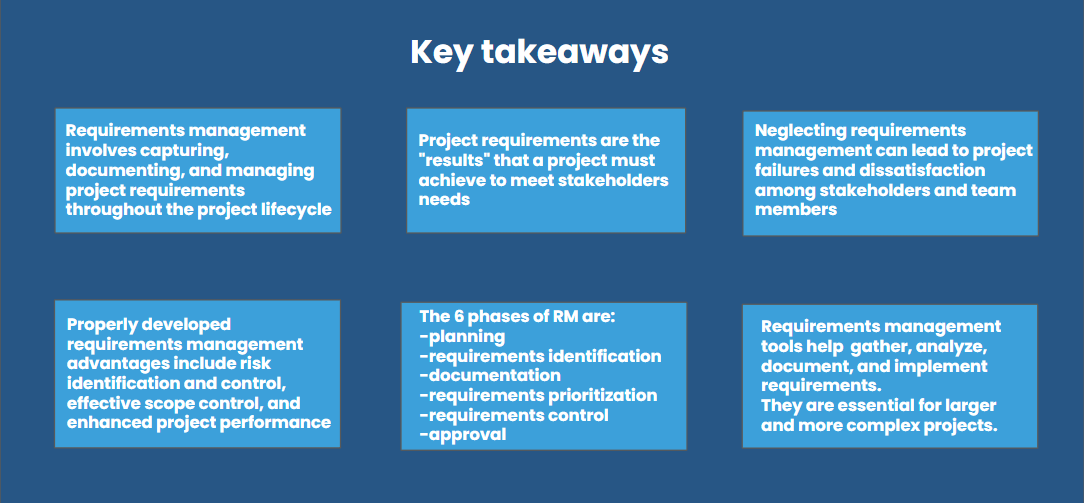
To summarize, requirements management is the method through which businesses identify, manage, verify, and evaluate proposals in order to satisfy stakeholder demands at each stage of the product lifecycle, from the initial conception of an idea through to its development and commercialization.
Requirements management's importance lies in the fact that a well-coordinated requirements management process is the difference between a successful project with satisfied stakeholders and a problematic project with ultimately unhappy stakeholders.
By following the six phases of requirements management, project teams can make sure that project needs are carefully planned, identified, recorded, prioritized, managed, authorized, and successfully communicated.
Project requirements management benefits greatly from the use of tools like IBM DOORS for requirements management. Teams may boost the likelihood of a project's success by utilizing these tools to accelerate the requirements management process, improve team management, encourage communication, and guarantee requirements compliance.
Softacus Services
If you don’t already have requirements management under control, we, at Softacus, are experts when it comes to consulting and service delivery of IBM software products and solutions in your business. We help our clients improve visibility and transparency when licensing and managing commercial software, providing measurable value while increasing efficiency and accountability. Contact us today so that we can get you on the right track toward guaranteed success in requirement management.
Related and Referenced Topics
Blog Articles:
Basics of Links and Link Types in IBM DOORS Next Generation - learn the basics about the linking and link types in IBM DOORS Next.
Linking Techniques in IBM DOORS Next - article explaining basic concepts and showing multiple ways of creation of links between artifacts.
Link By Attribute Feature in IBM DOORS Next - the article explains how to use the "Link by attribute" function to automatically create, update, or delete one or more links between artifacts based on values in the attributes of the artifact.
Softacus Widgets:
Link Switcher - widget developed by Softacus, that converts the context of artifacts links in a very short time.
Module Link Statistics - extension that provides users with a quick overview of the amount of the links in specific link types in a module.
Link Type Change- extension developed by Softacus designed to enhance the functionality of DOORS Next Generation by allowing users to manipulate the direction of a link or convert it to another type of link.
Links Builder- extension that allows the users to create a link between two artifacts in DOORS Next Generation according to the certain rules.
Link by Foreign Attribute - this extension allows users to create links between artifacts in the selected module(s), based on the attributes values.
Show Attributes of Linked Artifacts - this extension shows the attributes and links of the artifact that is currently selected.




